Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (17): 2685-2690.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.17.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Accurate positioning way to modify minimally invasive incision in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation
Liang Chang-xiang, Zheng Xiao-qing, Chang Yun-bing, Gu Hong-lin, Huang Shuai-hao
- Department of Orthopaedics, Guangdong General Hospital, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2014-02-10Online:2014-04-23Published:2014-04-23 -
Contact:Chang Yun-bing, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Guangdong General Hospital, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Liang Chang-xiang, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopaedics, Guangdong General Hospital, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Chang-xiang, Zheng Xiao-qing, Chang Yun-bing, Gu Hong-lin, Huang Shuai-hao. Accurate positioning way to modify minimally invasive incision in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(17): 2685-2690.
share this article
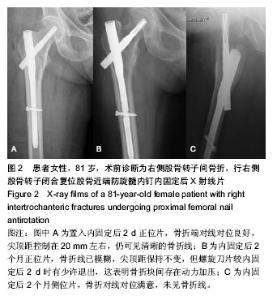
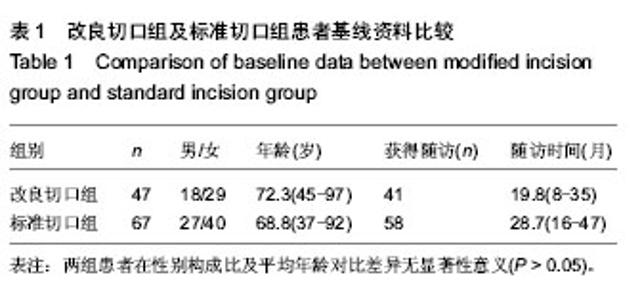
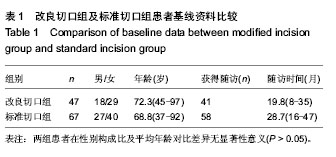
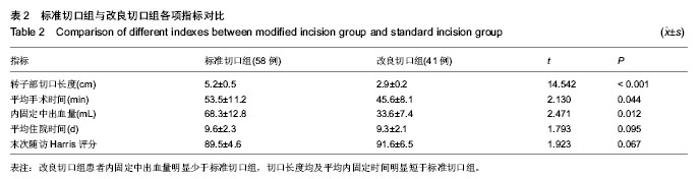
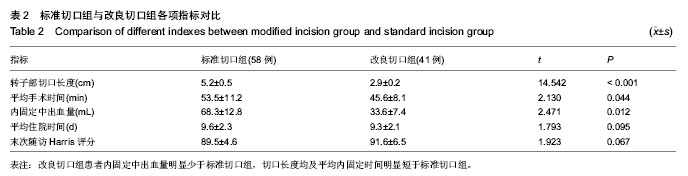
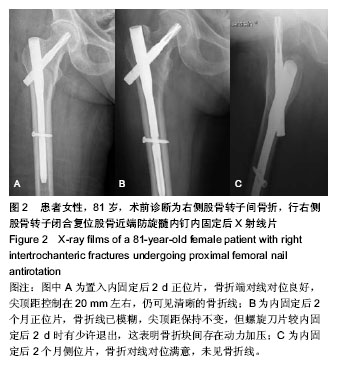
2.4 不良反应 两组患者均未发生内植物周围骨折、重要神经血管损伤。内固定后无切口感染、内植物断裂、内植物切割出股骨头及骨折端移位等情况。将两组患者的其他并发症一并统计,其中1例患者出现再次跌倒导致假体远端骨折,入院后行骨折复位钢板内固定;2例患者出现内固定后下肢轻度肿胀,下肢血管B超未发现静脉血栓形成,予抬高患者及静脉泵对症治疗后好转;1例患者内固定后出现脑梗死,转神内科对症治疗后好转,随访时残留轻度的患侧偏瘫;2例患者出现肺部感染、1例患者出现泌尿系感染,经抗感染等对症治疗后治愈。 2.5 典型病例介绍 患者女性,81岁,术前诊断为左股骨转子间骨折,行股骨转子闭合复位股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定。置入内固定后2 d正位片,骨折端对线对位良好,尖顶距控制在20 mm左右,仍可见清晰的骨折线(图2A);内固定后2个月正位片,骨折线已模糊,尖顶距保持不变,但螺旋刀片较内固定后2 d时有少许退出,这表明骨折块间存在动力加压(图2B);内固定后2个月侧位片,骨折对线对位满意,未见骨折线(图2C)。"
| [1] Harris WH. Traumatic Arthritis of the Hip After Dislocation and Acetabular Fractures: Treatment by Mold Arthroplasty: an End-result Study Using a New Method of Result Evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg.1969;51(4):737–755. [2] Campbell WC. 坎贝尔骨科手术学[M].卢世璧,王继芳,王岩,译. 10版.济南:山东科学技术出版社,2005: 2759-2762. [3] Kammerlander C, Gebhard F, Meier C, et al. Standardised cement augmentation of the PFNA using a perforated blade: A new technique and preliminary clinical results. A prospective multicentre trial. Injury. 2011;42(12):1484-1490. [4] Garg B, Marimuthu K, Kumar V. Outcome of short proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw for fixation of unstable trochanteric fractures. A randomised prospective comparative trial. Hip Int. 2011;21(5):531-536. [5] 原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年).中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011, 4(1): 2-17. [6] Bonnaire F,Lein T,Bula P.Trochanteric femoral fractures: anatomy, biomechanics and choice of implants. Unfallchirurg. 2011;114(6): 491-500. [7] Kristek D, Lovri? I, Kristek J,et al. The proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in the treatment of proximal femoral fractures. Coll Antropol. 2010;34(3):937-940. [8] 董纪元,李国宏,胡永成.老年人股骨转子间骨折围手术期的治疗分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(8):476-479. [9] Parker MJ, Bowers TR, Pryor GA. Sliding hip screw versus the Targon PF nail in the treatment of trochanteric fractures of the hip: a randomised trial of 600 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(3): 391-397. [10] Sahin S, Ertürer E, Oztürk I,et al. Radiographic and functional results of osteosynthesis using the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in the treatment of nstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44(2):127-134. [11] Elis J, Chechik O, Maman E, et al.Expandable proximal femoral nails versus 95° dynamic condylar screw-plates for the treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2012;43(8):1313- 1317. [12] Aros B, Tosteson AN, Gottlieb DJ,et al. Is a sliding hip screw or im nail the preferred implant for intertrochanteric fracture fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11): 2827-2832. [13] Park SY,Yang KH,Yoo JH,et al.The treatment of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures with the intramedullary hip nail. J Trauma. 2008;65(4): 852-857. [14] Nikoloski AN, Osbrough AL, Yates PJ. Should the tip-apex distance (TAD) rule be modified for the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA)? A retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013 Oct 17;8(1):35. [15] Kumbaraci M, Karapinar L, Incesu M. Treatment of bilateral simultaneous subtrochanteric femur fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in a patient with osteopetrosis: case report and review of the literature. J Orthop Sci. 2013 May;18(3):486-489. [16] Wild M, Jungbluth P, Thelen S, et al. The dynamics of proximal femoral nails: a clinical comparison between PFNA and Targon PF. Orthopedics. 2010;33(8): 204-207. [17] Tang SL,Jiang C.Comparison of the effect of inverted less invasive stabilization system (LISS) and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) in the treatment of complex unstable intertrochanteric fracture in aged. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011; 24(5): 366-369. [18] Palm H, Lysen C, Krasheninnikoff M,et al. Intramedullary nailing appears to be superior in pertrochanteric hip fractures with a detached greater trochanter: 311 consecutive patients followed for 1 year. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(2): 166-170. [19] Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H,et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study. Injury. 2008;39(8): 932-939. [20] Boopalan PR, Oh JK, Kim TY,et al.Incidence and radiologic outcome of intraoperative lateral wall fractures in OTA 31A1 and A2 fractures treated with cephalomedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(11): 638-642. [21] Swinteck BJ, Phan DL, Jani J, et al. Biomechanical effects of hardware configuration after union of proximal femoral and shaftfractures. Bone Joint Res. 2012;1(6):104-110. [22] Lenich A, Mayr E, Ruter A, et al. First results with the trochanter fixation nail (TFN): a report on 120 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126(10): 706-712. [23] Wang WY, Yang TF, Liu L et al. A comparative study of ipsilateral intertrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures treated with long proximal femoral nail antirotation or plate combinations. Orthop Surg. 2012 Feb;4(1):41-46. [24] Bernstein J, Ahn J. Provider factors associated with intramedullary nail use for intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15): 2619-2620. [25] Chua IT, Rajamoney GN, Kwek EB. Cephalomedullary nail versus sliding hip screw for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2013;21(3):308-312. [26] 姜磊,禹宝庆,傅青格.闭合复位PFN治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的体会[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2006,21 (1):59 - 62. [27] Zeng C, Wang YR, Wei J, et al. Treatment of trochanteric fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation or dynamic hip screw systems: a meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2012;40(3):839-851. [28] Kammerlander C, Gebhard F, Meier C,et al. Standardised cement augmentation of the PFNA using a perforated blade: A new technique and preliminary clinical results. A prospective multicentre trial. Injury. 2011;42(12): 1484-1490. [29] Mereddy P, Kamath S, Ramakrishnan M,et al. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2009;40(4):428-432. [30] Brunner A, Jöckel JA, Babst R. The PFNA proximal femur nail in treatment of unstable proximal femur fractures--3 cases of postoperative perforation of the helical blade into the hip joint. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(10):731-736. [31] Kraus M, Krischak G, Wiedmann K, et al. Clinical evaluation of PFNA® and relationship between the tip-apex distance and mechanical failure. Unfallchirurg. 2011;114(6):470-478. [32] De Bruijn K, den Hartog D, Tuinebreijer W, et al. Reliability of predictors for screw cutout in intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(14):1266-1272. [33] Stern R, Lübbeke A, Suva D,et al. Prospective randomised study comparing screw versus helical blade in the treatment of low-energy trochanteric fractures. Int Orthop. 2011;35(12): 1855-1861. [34] Hong JY, Suh SW, Park JH, et al. Comparison of soft-tissue serum markers in stable intertrochanteric fracture: dynamic hip screw versus proximal femoral nail-A preliminary study. Injury. 2011;42(2):204-208. [35] Wu CC, Tai CL. Effect of lag-screw positions on modes of fixation failure in elderly patients with unstableintertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2010;18(2):158-165. [36] Forte ML, Virnig BA, Eberly LE, et al. Provider factors associated with intramedullary nail use for intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 ;92(5):1105-1114. [37] Lee PC, Hsieh PH, Chou YC, et al. Dynamic hip screws for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients--encouraging results with a cement augmentation technique. J Trauma. 2010;68(4):954-964. [38] Kleweno C, Morgan J, Redshaw J, et al. Short versus Long Cephalomedullary Nails for the Treatment of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures in Patients over 65 Years. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;26(10): 726-729. [39] Dhamangaonkar AC, Joshi D, Goregaonkar AB, et al. Proximal femoral locking plate versus dynamic hip screw for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2013;21(3):317-322. |
| [1] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [2] | Fu Jiaxin, Xiao Lianping, Wang Shusen, Li Xiaodong, Han Liqiang, Wang Tonghao. Therapeutic effects of paraspinal approach combined with internal fixation through pedicle of fractured vertebra versus traditional AF screw-rod system for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1177-1181. |
| [3] | Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195. |
| [4] | Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202. |
| [5] | Fan Zhirong, Peng Jiajie, Zhong Degui, Zhou Lin, Su Haitao, Huang Yongquan, Wu Jianglin, Liang Yihao. Suture anchor combined with open reduction and internal fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for ankle fracture combined with deltoid ligament injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1307-1312. |
| [6] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [7] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [8] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [9] |
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming.
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3924-3930.
|
| [10] | Hao Liang, Zhang Zhonglin, Wang Baodong, Bi Zhenggang. Intertrochanteric fracture of the femur: improvement of internal fixation device, surgical changes and related disputes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2927-2935. |
| [11] | Yao Liquan, Ling Qinjie, Li Jiaying, Zhong Letian, Zhou Xingping, Liu Jintao, He Erxing, Yin Zhixun. Antibiotic artificial bone implantation for treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2133-2139. |
| [12] | Gong Zhibing, Wu Zhaoke, Zhang Huantang, Xu Zhiqing, Zhuang Zhikun, Zhang Qianjin. Allogeneic cortical bone plate combined with locking plate for Vancouver type B1 and C osteoporotic periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1812-1817. |
| [13] | Li Xiaofeng, Xie Furong, Zhan Long, Yang Yuan. Design of locking compression plate through transoral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1824-1828. |
| [14] | Tian Youyong, Wang Zhiyong. Short-term follow-up of dynamic hip screw versus proximal femoral nail anti-rotation for type AO/OTA A1 intertrochanteric femoral fracture in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1834-1839. |
| [15] | Guo Jinchao1, Cao Yuan2, Huang Junling1, Ma Jiajia1, Ma Chuang1. Intertrochanteric femoral fractures: an epidemiological analysis of 618 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(12): 1840-1845. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||